RGB Colour Sensor (TCS3472)
Summary
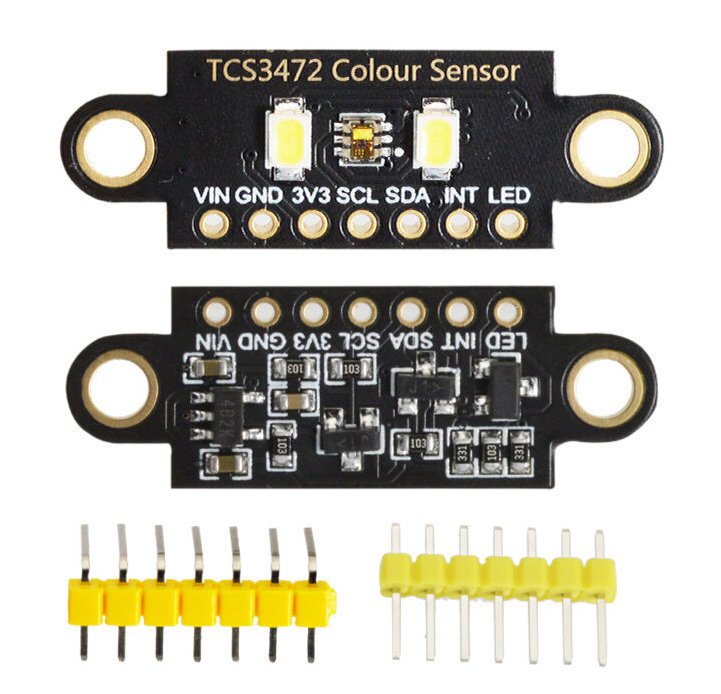
The circuit board is based on the TCS3472 chipset. This sensor is able to detect color value and return RGB data as response. The TCS3472 chipset has an integrated array of 3*4 filtered photodiodes and 16 bit analog-to-digital embedded converters. Of the 12 photodiodes, 3 have red filters, 3 have green filters, 3 have blue filters and 3 have no filter (clear), which gives a total range of RGBA (RGB + Transparency). When detecting the color of an object the TCS3472 returns data from four corresponding channels: red(R), green(G), blue(B) and clear(C)(non-filtered). The response from the red, green and blue channels (RGB) can be used to determine a particular source’s chromaticity.
An integrated infrared blocking filter minimises the infrared and UV spectral components of incident light and helps with accurate color measurement. The module has a working voltage of 3.3V/5V, and communicates through an I2C interface.
The TCS3472 Color Sensor board has 7 pins:
VIN: Module power supply of 5 V
GND: Ground
3V3: Low voltage module power supply of 3.3 V
SLC: I2C Clock
SDA: I2C data
INT: Adjust I2C Address
LED: Turning on the LED
When connected to the Arduino I2C bus, XOD patches can read off a series of calibrated values including: the intensity of light in the blue part of the spectrum (465nm), green (525nm) and red (615nm). In addition, the intensity of unfiltered clear light, illuminance value in lux and colour temperature (degrees K) can be read out.
How to Connect
To connect to the Grove board:
Connect four wires to pins inside one of the I2C sockets on the central portion of the board (top right)
Connect left-most wire (GND) to GND pin on module
Connect the second-left wire (VCC) to VCC pin on module
Connect the second-right wire (SDA) to SDA pin on module
Connect the right-most wire (SCL) to SCL pin on module
How to use in XOD
First, the external XOD library antoniorrg/tcs34725 should be loaded in the XOD environment. This library provides nodes and example patches that allow operation of the sensor. The contents of the library is show below, and a node for reading the TCS3472 sensor is shown right.
Test patch:
Notes
Colour recognition with the TCS3472: https://www.hackster.io/t3486784401/color-recognition-piano-62a16e
Characterisation of soil properties using a simple colour detection device: https://www.hackster.io/antonio-ruiz/characterisation-of-soil-properties-using-a-simple-device-6cce9b
Professional Hydroponics Light Monitoring: https://www.hackster.io/chuygen/professional-hydroponics-light-monitoring-3547dd
Multiplexing 6 I2C TCS34725 Color Sensors: https://www.hackster.io/sherwinchiu89/multiplexing-6-i2c-tcs34725-color-sensors-2a7272
Technical description for measuring color temperature with trhe TCS3472: https://circuitcellar.com/research-design-hub/projects/white-hot-measuring-color-temperature/